In today’s fast-paced world, understanding your health risks is crucial for maintaining well-being and preventing chronic diseases. Health Risk Assessments (HRAs) serve as a vital tool in identifying potential health issues before they become serious concerns. By evaluating lifestyle choices, medical history, and biometric data, HRAs empower individuals and healthcare providers to make informed decisions for better health outcomes.
📌 What is a Health Risk Assessment?
A Health Risk Assessment is a systematic approach used to evaluate an individual’s health status and potential risks. It typically involves:
- Questionnaires covering medical history, lifestyle habits, and family history.
- Biometric screenings such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and BMI measurements.
- Personalized feedback highlighting areas of concern and recommendations for improvement.
HRAs are commonly used in various settings, including:
- Workplace wellness programs to promote employee health.
- Primary care practices for preventive health planning.
- Public health initiatives to assess community health needs.
🧬 Components of a Health Risk Assessment
| Component | Description |
| Demographic Data | Age, gender, occupation, and other personal information. |
| Medical History | Past and current health conditions, surgeries, and medications. |
| Lifestyle Factors | Smoking status, alcohol consumption, diet, physical activity, and stress levels. |
| Biometric Data | Measurements such as blood pressure, cholesterol, glucose levels, and BMI. |
| Family History | Genetic predispositions to certain diseases, like diabetes or heart disease. |
📊 Benefits of Conducting a Health Risk Assessment
Implementing HRAs offers numerous advantages:
- Early Detection: Identifies risk factors for diseases like hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease.
- Personalized Health Plans: Tailors recommendations based on individual risk profiles.
- Enhanced Patient Engagement: Encourages individuals to take an active role in their health.
- Cost Savings: Reduces healthcare costs by preventing disease progression.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Provides valuable data for healthcare providers to make informed decisions.
🧪 Common Health Risk Assessment Tools
| Tool Name | Purpose |
| Framingham Risk Score | Estimates 10-year cardiovascular risk. |
| Gail Model | Assesses breast cancer risk in women. |
| Diabetes Risk Calculator | Evaluates the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes. |
| Your Disease Risk | Provides risk assessments for various chronic diseases. |
| Health Risk Appraisal (HRA) Tools | Comprehensive assessments are used in workplace wellness programs. |
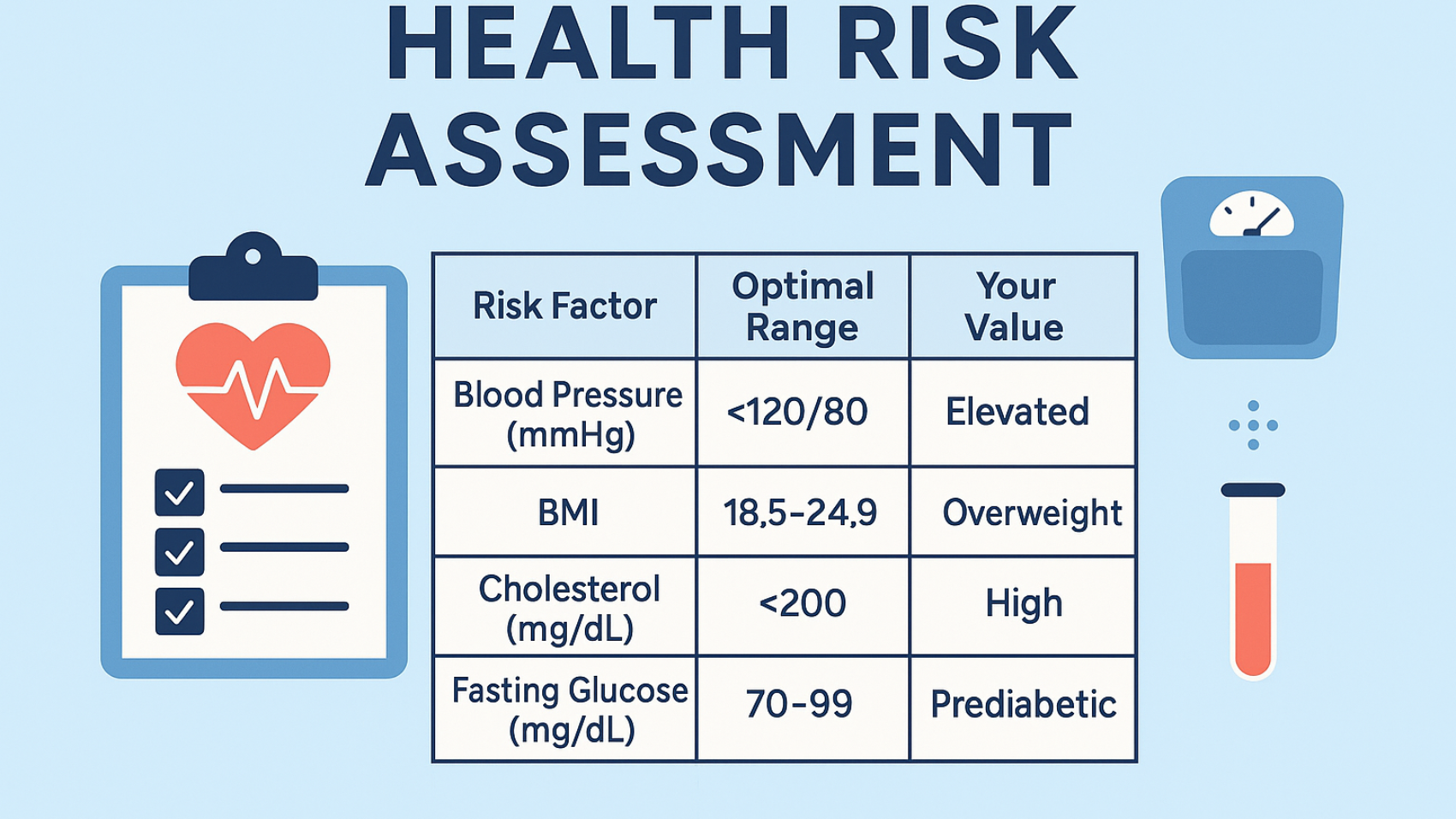
📈 Sample Health Risk Assessment Chart
| Risk Factor | Optimal Range | Your Value | Risk Level |
| Blood Pressure (mmHg) | <120/80 | 130/85 | Elevated |
| BMI | 18.5–24.9 | 27.5 | Overweight |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | <200 | 220 | High |
| Fasting Glucose (mg/dL) | 70–99 | 105 | Prediabetic |
Note: This is a sample chart. Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized assessments.
🧠 Implementing HRAs in Workplace Wellness Programs
Employers can leverage HRAs to foster a healthier workforce:
- Confidential Assessments: Ensure employee privacy while collecting health data.
- Customized Wellness Plans: Develop programs targeting common risk factors identified in HRAs.
- Incentive Programs: Encourage participation through rewards for completing HRAs and achieving health goals.
- Monitoring Progress: Use follow-up assessments to track improvements and adjust programs accordingly.
📲 Digital Tools and Applications for Health Risk Assessments
With technological advancements, various digital platforms facilitate HRAs:
- Online Questionnaires: Accessible tools for individuals to assess their health risks conveniently.
- Mobile Apps: Provide real-time tracking of health metrics and personalized recommendations.
- Integrated Health Systems: Allow healthcare providers to access and analyze patient data efficiently.
🧭 Steps to Conduct a Health Risk Assessment
- Preparation: Gather necessary information, including medical history and lifestyle habits.
- Assessment: Complete the HRA questionnaire and biometric screenings.
- Analysis: Review the results to identify potential health risks.
- Action Plan: Develop strategies to mitigate identified risks, such as lifestyle modifications or medical interventions.
- Follow-Up: Regularly monitor progress and adjust the action plan as needed.
📚 Conclusion
Health Risk Assessments are invaluable tools in the proactive management of personal and community health. By identifying potential risks early, individuals can take informed steps toward healthier lifestyles, and healthcare providers can tailor interventions effectively. Embracing HRAs contributes to improved health outcomes and a reduction in preventable diseases.